- Published on
Adding Design-by-Contract [[invariant]] conditions to C++, via a GCC plugin
- Authors

- Name
- Gavin Ray
- @GavinRayDev
Table of Contents
Note: You can find the source code for this project here: https://github.com/GavinRay97/gcc-invariant-plugin
Preface
Last month, GCC landed support for Contracts in trunk:
If you aren't a C++ developer, or you are a C++ developer but haven't followed the Contracts feature/don't have an interest in Design-by-Contract, what this proposal does is allow you to annotate your functions with pre/post conditions that are checked when the method is called.
A trivial example might be something like:
int divide_returns_gt_10(int a, int b)
[[pre: a > 0 && b > 0]] // Avoid dividing by zero
[[post r: r > 10]] // Enforce that we return > 10
{
return a / b;
}
This functionality is fantastic because it allows you to encode your requirements and assertions declaratively into your methods.
But, the most powerful feature of Design-by-Contract is the invariant. An invariant condition allows you to write a set of assertions/assumptions about the state of an object/program that should always hold true.
Invariants are incredibly useful for enforcing properties of systems, or data structures. Especially when the validity of a data structure requires conforming to a set of properties.
A compelling usecase
In my free time over the last 6-8 months, I've been writing a database from scratch.
As a highschool dropout, this experience has been... a lot different than what I thought it would be.
There are many things you pick up as part of a CS degree that (I now know) are assumed knowledge when working on databases. One of those things is the family of B-Trees.
Like many folks, I'm on holiday, and it's been a great time for study. Except I've grown exceedingly infuriated at my own seeming inability to do basic CS tasks. Like write a proper B+ Tree:
If anyone reads my feed and thinks:
"Oh hey this person knows stuff"
Here's what you don't see: I've spent the first +20 hours of my Xmas vacation trying to write a B+ Tree and ending up with... this
The Spaghetti Syndr... I mean, Impasta Syndrome is real pic.twitter.com/qOfsy34YyS
— Gavin Ray (@GavinRayDev)
December 28, 2022
My code had all the shape and feel of a tree-like structure, but it wasn't preserving the properties of a B+ Tree.
I was ending up with garbage, and not realizing it until I had visualized it with Graphviz! 🙁
Imagine if we had invariants that we could assert after every property change to the tree.
Below is an example of what an invariant implementation for a B-Tree data structure might look like:
struct BTree
{
[[invariant]]
void check_invariants() { check_node_invariants(root); }
// According to Knuth's definition, a B-tree of order "m" is a tree which satisfies the following
// properties:
//
// - Every node has at most "m" children.
// - Every internal node has at least ⌈m/2⌉ children.
// - Every non-leaf node has at least two children.
// - All leaves appear on the same level.
// - A non-leaf node with k children contains k−1 keys.
void check_node_invariants(Node* node)
{
if (node == nullptr)
return;
// Every node has at most "m" children.
assert(node->num_children <= MAX_VALUES + 1);
// Every internal node has at least ⌈m/2⌉ children.
if (node->is_internal())
assert(node->num_children >= MIN_VALUES);
// Every non-leaf node has at least two children.
if (!node->is_leaf())
assert(node->num_children >= 2);
// A non-leaf node with k children contains k−1 keys.
if (!node->is_leaf())
assert(node->num_children == node->num_values + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < node->num_children; i++)
check_node_invariants(node->children[i]);
}
};
Now, assuming that this check_invariants method is called any time that our B-Tree changes, we can be 100% sure that it's a proper B-Tree.
Super powerful!
The rest of this article will walk through what it means to make this sentence come to life:
Now, assuming that this
check_invariantmethod is called any time that our B-Tree changes...
Developing the GCC Plugin
There are a few things to be said about developing GCC plugins:
- Documentation is essentially non-existent
- There are few people with experience working with the GCC IR API's (GIMPLE/RTL etc)
- Most of existing plugins and examples you can find online have to do with analysis, and so show read-only usage of the API's.
The following code is cobbled together primarily from examples taken from these two blogposts:
- https://gabrieleserra.ml/blog/2020-08-27-an-introduction-to-gcc-and-gccs-plugins.html
- https://stephanfr.blog/2013/05/19/building-gcc-plugins-part-1-c-11-generalized-attributes/
The working code for insertion of the check_invariants statements was a stroke of dumb luck after 15 hours, from one of the suggestions given by Github Copilot.
(More on this later. I'm not fully happy with the insertion code, because it depends on implicit fallback to the this-> member namespace rather than an explicit call)
With that said, let's begin!
Setting Up
If you're following along at home (this will be an easy one, it requires just a CMakeLists.txt and a single .cpp file), this is the CMake definition we'll be using to build and test our plugin code:
project(gcc-invariant-plugin)
set(CMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS ON)
set(G++_COMPILER /usr/local/gcc-dev/bin/g++)
set(GCC_PLUGIN_DIR /usr/local/gcc-dev/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/13.0.0/plugin)
add_library(gcc-invariant-plugin SHARED src/plugin.cpp)
target_compile_options(gcc-invariant-plugin PRIVATE -fno-rtti)
target_include_directories(gcc-invariant-plugin PRIVATE ${GCC_PLUGIN_DIR}/include)
# Copy compile_commands.json to root directory if changed
add_custom_command(TARGET gcc-invariant-plugin POST_BUILD
COMMAND ${CMAKE_COMMAND} -E copy_if_different
${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/compile_commands.json
${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/compile_commands.json
)
# Command to run GCC with the build plugin using "-fplugin=./libgcc-invariant-plugin.so"
add_custom_target(run-gcc ALL
COMMAND ${G++_COMPILER} -fplugin=./libgcc-invariant-plugin.so -std=c++20 -O0 -g -ggdb3 -fcontracts
-o ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/test-binary
${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/test/test.cpp
DEPENDS gcc-invariant-plugin
WORKING_DIRECTORY ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}
)
This assumes a directory layout like:
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── src
│ └── plugin.cpp
└── test
└── test.cpp
Initial Skeleton
Now, we can mimic the structure of Gabriele's plugin, with some slight changes and using the scoped-plugin sample from Stephan's post. This is so that we can call our attribute [[demo::invariant]] to distinguish it from a language-level attribute.
What we want is to create a skeleton plugin that does two things:
- Create a new custom attribute,
[[demo::invariant]]that we can use and check for the existence of - Hook into the parsing of struct/class member functions, and performs some "Hello-world" like behavior to check that it's working as intended
With these two things, we would have much of the ingredients needed for adding invariant support to C++!
To do this, looks something like the below:
- First, we include some order-sensitive (hooray!) headers:
// These includes are order-sensitive. GCC, am I right?...
// clang-format off
#include <gcc-plugin.h>
#include <context.h>
#include <plugin-version.h>
#include <tree.h>
#include <gimple.h>
#include <tree-pass.h>
#include <attribs.h>
#include <tree-pretty-print.h>
#include <plugin.h>
#include <cp/cp-tree.h>
// clang-format on
- Next, we define some general configuration settings for our plugin:
namespace
{
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// GCC PLUGIN SETUP (BASIC INFO / LICENSE / REQUIRED VERSION)
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
constexpr auto DEBUG = 1;
constexpr auto ATTRIBUTE_NAME = "invariant";
constexpr auto PLUGIN_VERSION = "0.1";
constexpr auto PLUGIN_HELP = "This plugin instruments functions with the invariant attribute";
constexpr auto PLUGIN_NAME = "invariant_plugin";
constexpr auto PLUGIN_GCC_BASEV = "13.0.0";
/**
* Additional information about the plugin. Used by --help and --version
*/
const struct plugin_info invariant_plugin_info = {
.version = PLUGIN_VERSION,
.help = PLUGIN_HELP,
};
/**
* Represents the gcc version we need. Used to void using an incompatible plugin
*/
const struct plugin_gcc_version invariant_plugin_version = {
.basever = PLUGIN_GCC_BASEV,
};
}; // namespace
- We define the configuration and callback handlers for a custom
[[demo::invariant]]attribute (this does not register the attribute yet)
namespace
{
// <...>
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// GCC ATTRIBUTES MANAGEMENT (REGISTERING / CALLBACKS)
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Attribute handler callback
* @see Declared in tree-core.h
*/
tree
handle_invariant_attribute(tree* node, tree name, tree args, int flags, bool* no_add_attrs)
{
if constexpr (DEBUG == 1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "> Found attribute\n");
fprintf(stderr, "\tnode = ");
print_generic_stmt(stderr, *node, TDF_NONE);
fprintf(stderr, "\tname = ");
print_generic_stmt(stderr, name, TDF_NONE);
}
return NULL_TREE;
}
/**
* Structure describing an attribute and a function to handle it
* @see Declared in tree-core.h
* @note Refer to tree-core for docs about
*/
/* Attribute definition */
const struct attribute_spec invariant_attribute = {
// [[demo::invariant]]
.name = "invariant",
.min_length = 0,
.max_length = 0,
.decl_required = true,
.type_required = false,
.function_type_required = false,
.affects_type_identity = false,
.handler = handle_invariant_attribute,
.exclude = nullptr,
};
// The array of attribute specs passed to register_scoped_attributes must be NULL terminated
const attribute_spec scoped_attributes[] = {
invariant_attribute,
{ NULL, 0, 0, false, false, false, false, NULL, NULL }
};
/**
* Plugin callback called during attribute registration
*/
void
register_attributes(void* event_data, void* data)
{
warning(0, "Callback to register attributes");
register_scoped_attributes(scoped_attributes, "demo");
}
}; // namespace
- We define the configuration and handler for a GIMPLE pass, which we will eventually use to insert calls to the
[[demo::invariant]]-marked function. For now, it only prints out the name of member functions which should be processed.
namespace
{
// <...>
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// PLUGIN INSTRUMENTATION LOGIC
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* For each function lookup attributes and insert invariant function calls
*/
unsigned int
instrument_invariants_plugin_exec(void)
{
// get the FUNCTION_DECL of the function whose body we are reading
tree fndecl = current_function_decl;
// print the function name
fprintf(stderr, "> Inspecting function '%s'\n", IDENTIFIER_POINTER(DECL_NAME(fndecl)));
// If the method is not a member of a struct/class, then skip it.
if (TREE_CODE(DECL_CONTEXT(fndecl)) != RECORD_TYPE)
return 0;
fprintf(stderr, "\t - Found a member function of a struct/class\n");
return 0;
}
/**
* Metadata for a pass, non-varying across all instances of a pass
* @see Declared in tree-pass.h
* @note Refer to tree-pass for docs about
*/
const struct pass_data invariant_pass_data = {
.type = GIMPLE_PASS, // type of pass
.name = PLUGIN_NAME, // name of plugin
.optinfo_flags = OPTGROUP_NONE, // no opt dump
.tv_id = TV_NONE, // no timevar (see timevar.h)
.properties_required = PROP_gimple_any, // entire gimple grammar as input
.properties_provided = 0, // no prop in output
.properties_destroyed = 0, // no prop removed
.todo_flags_start = 0, // need nothing before
.todo_flags_finish =
TODO_update_ssa | TODO_cleanup_cfg // need to update SSA repr after and repair cfg
};
/**
* Definition of our invariant GIMPLE pass
* @note Extends gimple_opt_pass class
* @see Declared in tree-pass.h
*/
class invariant_gimple_pass : public gimple_opt_pass
{
public:
/**
* Constructor
*/
invariant_gimple_pass(const pass_data& data, gcc::context* ctxt)
: gimple_opt_pass(data, ctxt)
{
}
/**
* This is the code to run when pass is executed
* @note Defined in opt_pass father class
* @see Defined in tree-pass.h
*/
unsigned int execute(function* exec_fun) { return instrument_invariants_plugin_exec(); }
};
}; // namespace
- Finally, we define the entry point for the plugin,
plugin_init, which is called by GCC when the plugin is loaded. We register the attribute and the GIMPLE pass.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// PLUGIN INITIALIZATION
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
int plugin_is_GPL_compatible;
/**
* Initializes the plugin. Returns 0 if initialization finishes successfully.
*/
int
plugin_init(plugin_name_args* plugin_info, plugin_gcc_version* version)
{
if (!plugin_default_version_check(version, &gcc_version))
return 1;
register_callback(plugin_info->base_name, PLUGIN_INFO, NULL, (void*) &invariant_plugin_info);
printf("> plugin '%s @ %s' was loaded onto GCC\n", PLUGIN_NAME, PLUGIN_VERSION);
register_pass_info invariant_pass = {
.pass = new invariant_gimple_pass(invariant_pass_data, g),
.reference_pass_name = "ssa", // get called after GCC has produced SSA representation
.ref_pass_instance_number = 1, // after first opt pass to be sure opt will not throw away
.pos_op = PASS_POS_INSERT_AFTER,
};
register_callback(plugin_info->base_name, PLUGIN_PASS_MANAGER_SETUP, NULL, &invariant_pass);
register_callback(plugin_info->base_name, PLUGIN_ATTRIBUTES, register_attributes, NULL);
return 0;
}
Testing the Skeleton
Now that we have the bare-bones outline of the plugin, lets create a test-case file that we'll use throughout the rest of this post, and run the plugin against it.
// test/test.cpp
#include <cassert>
#include <iostream>
class Stack
{
private:
static constexpr int MAX_SIZE = 100;
int top = 0;
int old_top = 0;
int data[MAX_SIZE];
[[demo::invariant]]
void check_invariants()
{
// I know this invariant/assertion is useless in combination with the [[pre]]/[[post]] conditions
// I just wanted to show a combination use of [[invariant]] and [[pre]]/[[post]] con
assert(top >= 0 && top <= MAX_SIZE);
}
public:
bool empty() const { return top == 0; }
bool full() const { return top == MAX_SIZE; }
void push(int value)
[[pre: !full()]]
[[post: top == old_top + 1]]
{
data[top++] = value;
old_top = top;
}
int pop()
[[pre: !empty()]]
[[post: top == old_top - 1]]
{
old_top = top;
return data[--top];
}
};
int main()
{
Stack stack;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
stack.push(i);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
std::cout << stack.pop() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
If we run cmake --build ./build --target run-test we should see:
[build] <built-in>: warning: Callback to register attributes
[build] > Found attribute
[build] node = check_invariants
[build] name = invariant
[build] > Inspecting function 'push'
[build] - Found a member function of a struct/class
[build] > Inspecting function 'pop'
[build] - Found a member function of a struct/class
[build] > Inspecting function 'pop'
[build] - Found a member function of a struct/class
[build] > Inspecting function 'empty'
[build] - Found a member function of a struct/class
[build] > Inspecting function 'full'
[build] - Found a member function of a struct/class
[build] > Inspecting function 'push'
[build] - Found a member function of a struct/class
[build] > Inspecting function 'pop'
[build] - Found a member function of a struct/class
[build] > Inspecting function '__ct_base '
[build] - Found a member function of a struct/class
[build] > Inspecting function 'main'
[build] > plugin 'invariant_plugin @ 0.1' was loaded onto GCC
[build] [2/2] cd /home/user/projects/gcc-invariant-plugin/build/default && /home/user/projects/gcc-invariant-plugin/test-binary
[build] 99
[build] 98
...
[build] 1
[build] 0
[build] Build finished with exit code 0
Hooray!
Implementing the [[invariant]] call code-generation
Now, we need to implement the logic to to insert calls to the member function marked [[demo::invariant]] (if any exists) in all other member functions of any class/struct which contains an invariant function.
There are a few nuances to this:
- We don't want to insert at the beginning of constructors, because fields won't have been initialized yet.
- We don't want to insert calls at the end of destructors, because fields will have been destroyed
- There are probably others I haven't thought about
But other than that, I've implemented it as inserting at both the beginning and end of the function (before the return, if it exists)
Below is the code to do this:
👇 CLICK TO EXPAND CODE 👇
unsigned int
instrument_invariants_plugin_exec(void)
{
// get the FUNCTION_DECL of the function whose body we are reading
tree fndecl = current_function_decl;
// print the function name
fprintf(stderr, "> Inspecting function '%s'\n", FN_NAME(fndecl));
// If the method is not a member of a struct/class, then skip it.
if (TREE_CODE(DECL_CONTEXT(fndecl)) != RECORD_TYPE)
return 0;
// Try to locate the [[invariant]] function
tree invariant_fn = NULL_TREE;
// Iterate over every member function of the class
for (tree f = TYPE_FIELDS(DECL_FIELD_CONTEXT(fndecl)); f != NULL_TREE; f = DECL_CHAIN(f))
{
if (TREE_CODE(f) == FUNCTION_DECL)
{
// Check if the function has an [[invariant]] attribute
tree attrs = DECL_ATTRIBUTES(f);
for (tree attr = attrs; attr != nullptr; attr = TREE_CHAIN(attr))
{
// Check if attribute name is "invariant"
if (get_attribute_name(attr) == get_identifier("invariant"))
{
invariant_fn = f;
}
}
}
}
if (invariant_fn == NULL_TREE)
return 0;
// If the method name is the same as the [[invariant]] attribute function, then skip it.
if (DECL_NAME(fndecl) == DECL_NAME(invariant_fn))
return 0;
// attribute was in the list
fprintf(stderr, "\t attribute %s found! \n", ATTRIBUTE_NAME);
// get function entry block
basic_block entry = ENTRY_BLOCK_PTR_FOR_FN(cfun)->next_bb;
auto insert_invariant_calls_intelligently = [&] {
// get the first statement
gimple* first_stmt = gsi_stmt(gsi_start_bb(entry));
// Skip if this is a constructor, because fields will not be initialized yet
if (DECL_CONSTRUCTOR_P(fndecl))
{
fprintf(stderr, "\t skipping constructor start invariant call\n");
return;
}
// warn the user we are adding an invariant function
fprintf(stderr, "\t adding function call before ");
print_gimple_stmt(stderr, first_stmt, 0, TDF_NONE);
// Insert the invariant call before the current statement
gimple_stmt_iterator gsi = gsi_for_stmt(first_stmt);
gsi_insert_before(&gsi, gimple_build_call(invariant_fn, 0), GSI_SAME_STMT);
// Skip if destructor, because fields will have been destroyed already
if (DECL_DESTRUCTOR_P(fndecl))
{
fprintf(stderr, "\t skipping destructor end invariant call\n");
return;
}
// Insert the invariant call at the end of the function, or before the return statement (if
// any)
gimple_stmt_iterator gsi2 = gsi_last_bb(ENTRY_BLOCK_PTR_FOR_FN(cfun)->next_bb);
gimple* last_stmt = gsi_stmt(gsi2);
// Double check to ensure that the last_stmt != first_stmt
if (first_stmt == last_stmt)
{
fprintf(stderr, "\t first and last statement are the same, skipping last statement\n");
return;
}
// If the last statement is a return statement, then insert before it
if (gimple_code(last_stmt) == GIMPLE_RETURN)
{
fprintf(stderr, "\t adding function call before ");
print_gimple_stmt(stderr, last_stmt, 0, TDF_NONE);
gsi_insert_before(&gsi2, gimple_build_call(invariant_fn, 0), GSI_SAME_STMT);
}
else
{
fprintf(stderr, "\t adding function call after ");
print_gimple_stmt(stderr, last_stmt, 0, TDF_NONE);
gsi_insert_after(&gsi2, gimple_build_call(invariant_fn, 0), GSI_SAME_STMT);
}
};
// Insert the invariant function calls at the beginning/end of fn bodies based on
// certain conditions (whether it's a ctor/dtor, etc.)
insert_invariant_calls_intelligently();
// done!
return 0;
}
Testing again, violating invariants
If we modify our test code so that the invariant is violated:
void check_invariants() { assert(top >= 0 && top <= 50); }
And then re-compile with our plugin:
[build] <built-in>: warning: Callback to register attributes
[build] > Found attribute
[build] node = check_invariants
[build] name = invariant
[build] > Inspecting function 'push'
[build] attribute invariant found!
[build] adding function call before retval.1_4 = Stack::full (this_2(D));
[build] adding function call after if (retval.1_4 != 0)
[build] > Inspecting function 'pop'
[build] attribute invariant found!
[build] adding function call before retval.2_4 = Stack::empty (this_2(D));
[build] adding function call after if (retval.2_4 != 0)
[build] > Inspecting function 'pop'
[build] attribute invariant found!
[build] adding function call before _1 = this_5(D)->top;
[build] adding function call after if (_1 != _3)
[build] > Inspecting function 'check_invariants'
[build] > Inspecting function 'empty'
[build] attribute invariant found!
[build] adding function call before _1 = this_3(D)->top;
[build] adding function call after _4 = _1 == 0;
[build] > Inspecting function 'full'
[build] attribute invariant found!
[build] adding function call before _1 = this_3(D)->top;
[build] adding function call after _4 = _1 == 100;
[build] > Inspecting function 'push'
[build] attribute invariant found!
[build] adding function call before Stack::push (this_7(D), value_8(D));
[build] adding function call before return;
[build] > Inspecting function 'pop'
[build] attribute invariant found!
[build] adding function call before Stack::pop (this_7(D));
[build] adding function call after _13 = _12;
[build] > Inspecting function '__ct_base '
[build] attribute invariant found!
[build] skipping constructor start invariant call
[build] > Inspecting function 'main'
[build] > plugin 'invariant_plugin @ 0.1' was loaded onto GCC
And run the test program, we should see:
[user@MSI gcc-invariant-plugin]$ ./test-binary
test-binary: /home/user/projects/gcc-invariant-plugin/test/test.cpp:13: void Stack::check_invariants(): Assertion `top >= 0 && top <= 50' failed.
Aborted
Et-voila! We've done it!
Checking the codegen in Ghidra
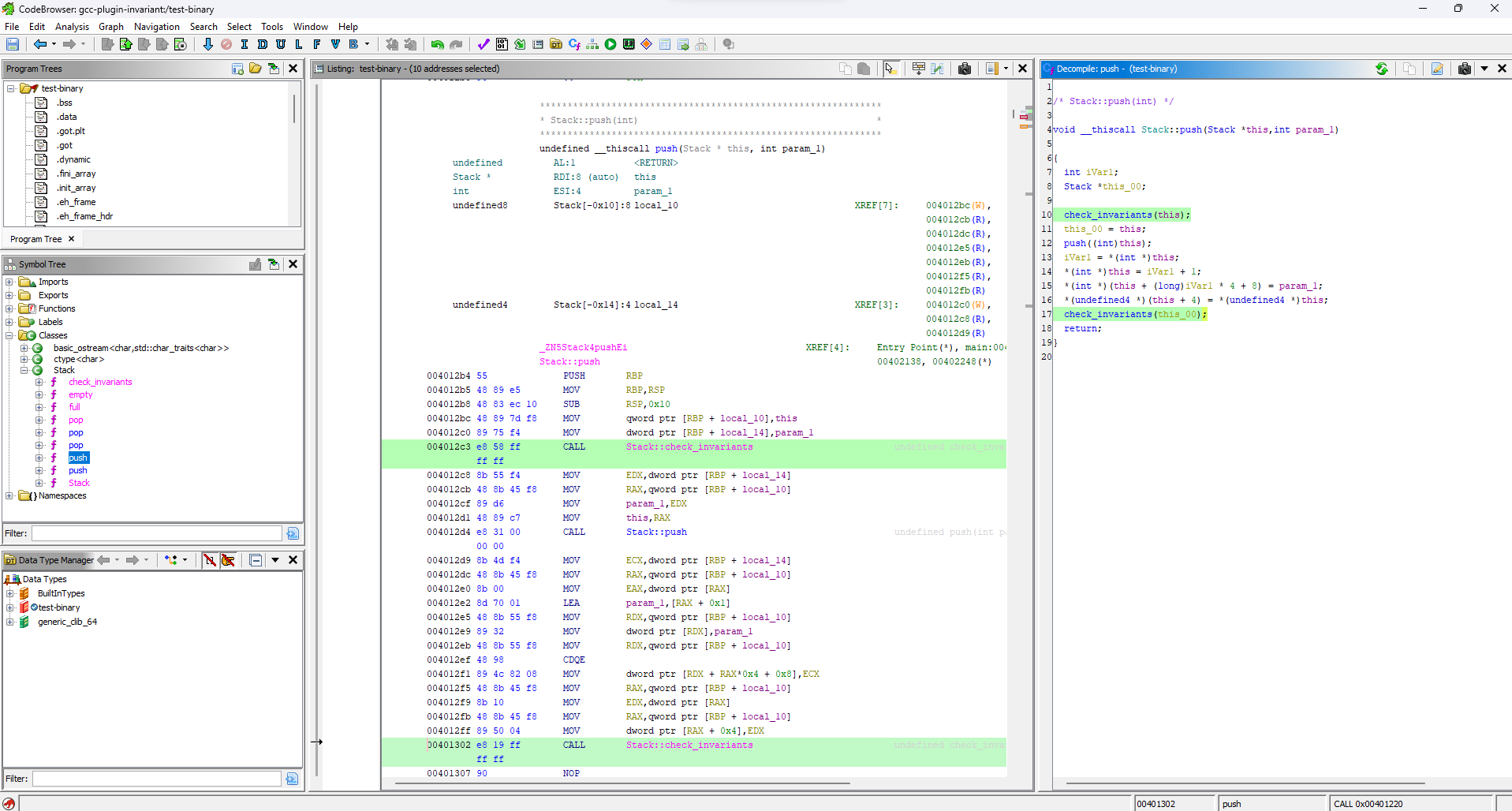
To be sure things have come out right, we can take a look at the compiled code in something like Ghidra.
Note: this is stepping outside of my forte, so there might be easier ways of doing this.
Opening test-binary in Ghidra, and checking the primary definition of Stack.push() (note that the pre/post contracts will also generate function entries) we should see the below:
Conclusions
So we have a plugin, and it technically works, and that's cool. Sweet!
But remember when I said above:
... I'm not fully happy with the insertion code, because it depends on implicit fallback to the
this->member namespace rather than an explicit call
With the current state of the plugin code, I'm still not fully satisfied with the GIMPLE calls used to invoke the invariant method.
I don't pretend to be an expert on C++. I think letting it look up the invariant function in the current scope/context is fine.
But what it should do is form an explicit member-function call to this->check_invariant();, which I burned some ~8 hours on trying to figure out.
A Request for Help
If anyone knows how to do this, please let me know. Submit an issue/PR, or reach out via email/Twitter.
I submitted questions to StackOverflow, reached out on the GCC mailing list, and even had a chat with Iain Buclaw, the maintainer of GDC (the D-language frontend for GCC).
Iain got me going down the right path I think, which I am pretty sure involves a combination of lookup_member() and build_new_method_call(), but I've not gotten it to work.
All the details are here in case anyone's interested in pursuing it further:
Thanks & Acknowledgement
I'd like to thank the following people:
- Iain Buclaw, for letting me bug him, and just generally maintaining the GDC compiler and helping with release management + infrastructure.
- The authors of these two blogposts:
Attribution
I "borrowed" the image in the OpenGraph metadata tag from the below blogpost, which is well-written and worth the read. I couldn't find any information on the page on whether it was copyright protected.
Hopefully the author doesn't mind, if they do I'll remove it!